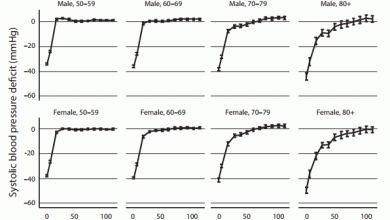
Hypertension is the most common modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular disease and death, and lowering blood pressure with antihypertensive drugs reduces target organ damage and prevents cardiovascular disease outcomes.
Most hypertensive patients will need a combination of antihypertensive agents to achieve the therapeutic goals. Recent guidelines recommend initiating treatment with two drugs in those patients with a systolic blood pressure >20 mmHg and/or a diastolic blood pressure >10 mmHg above the goals, and in those patients with high cardiovascular risk. In addition, approximately 25% of patients will require three antihypertensive agents to achieve the therapeutic targets.