Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a chronic and life-threatening disease characterised by progressive vascular remodelling that leads to increased pulmonary vascular resistance, right ventricular heart failure and death.
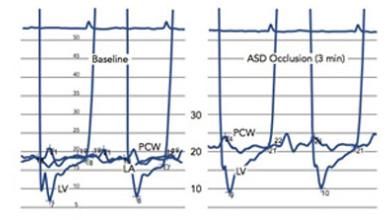
PAH is defined by >25 mmHg increase in pulmonary arterial blood pressure and a pulmonary capillary wedge pressure of 15 mmHg. If left untreated, PAH is fatal; it has a survival rate of just 34% after 5 years. Current therapies include stimulating the nitric oxide (NO)–soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC)–cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) axis, improving the prostacyclin pathway or inhibiting the endothelin pathway.