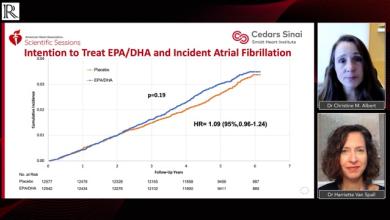
Electrophysiology has rapidly transformed from diagnostic cardiac studies to direct therapeutic interventions. Many cardiac arrhythmias that formerly required the use of drugs or surgery can now be routinely cured in the electrophysiology laboratory by means of transcatheter ablation techniques.
Clinical electrophysiological techniques have evolved for the assessment of sinus nodal, AV nodal and His-Purkinje system function. The evaluation of tachyarrhythmias has progressed rapidly, and pharmacological, device and surgical therapy can now be guided by electrophysiology of heart and arrhythmias studies.
Supraventricular arrhythmias can exacerbate the heart failure symptoms by decreasing the effective cardiac output and control requires pharmacological, electrical or catheter-based intervention.
In patients with atrial flutter or atrial fibrillation, anticoagulation is paramount to prevent systemic or cerebral embolism. People with heart failure are also prone to develop ventricular arrhythmias that can present a challenge to the clinician. The management strategy depends on the type of arrhythmia, the underlying structural heart disease and the severity of heart failure.