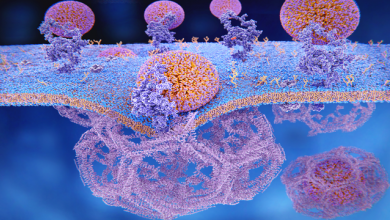
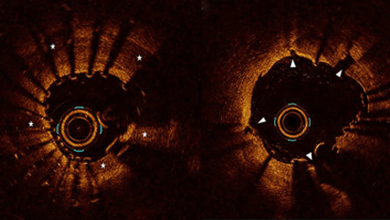
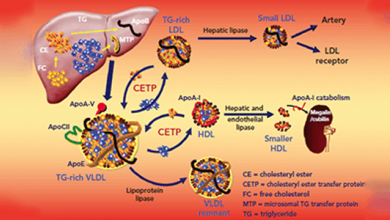
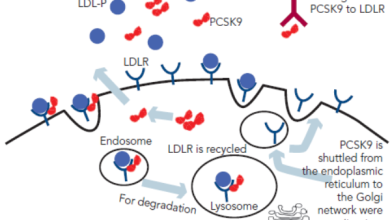
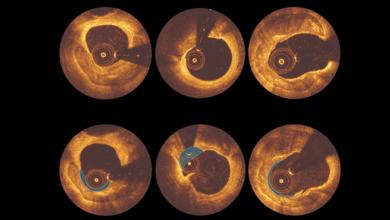
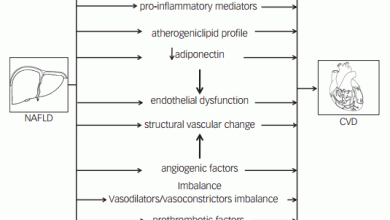
Substantial progress in the treatment of atherosclerotic complications – in particular in secondary prevention – has led to a significant reduction of recurrent cardiovascular events. This has been through the use of pharmacological strategies including lipid-lowering drugs such as statins, beta-blockers, angiotensin-converting ensyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers, along with the introduction of early percutaneous coronary intervention in acute coronary syndrome with consecutive application of dual antiplatelet therapy.
Close Menu
View all - Electrophysiology & Arrhythmia
Atrial Arrhythmias
Atrial Fibrillation
Catheter Ablation of Cardiac Arrhythmias
Persistant AF using Cryoballoon
Real World Contact Force Ablation
Pacing, Defibrillators and Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy
Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation
Reversal Agents
Ventricular Arrhythmias
Supraventricular Tachycardia
Sudden Cardiac Death
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis
Read time: 1h 1m 1s
About
Media
Media
Watch time: 4m 53s
Watch time: 4m 57s
Watch time: 8m 2s
Watch time: 3m 25s
Watch time: 4m 43s
Watch time: 4m 14s
Watch time: 7m 48s
Watch time: 7m 44s
Watch time: 9m 40s
Articles
Time to Act - Guideline-defined Treatment Goals for Cardiovascular Risk Factors Are Not Achieved in Primary Care
Citation:
European Cardiology 2008:4(2):24-6
- Abstract
- Full text
- Login or register to view PDF.
- Permissions
- References
Permissions×
For commercial reprint enquiries please contact Springer Healthcare: ReprintsWarehouse@springernature.com.
For permissions and non-commercial reprint enquiries, please visit Copyright.com to start a request.
For author reprints, please email rob.barclay@radcliffe-group.com.
For permissions and non-commercial reprint enquiries, please visit Copyright.com to start a request.
For author reprints, please email rob.barclay@radcliffe-group.com.
- Views:
 282
282
- Downloads:
 0
0
- Citations: 1
Menopause, Cholesterol and Cardiovascular Disease
Citation:
US Cardiology 2008;5(1):12–4
- Abstract
- Full text
- Login or register to view PDF.
- Permissions
- References
Permissions×
For commercial reprint enquiries please contact Springer Healthcare: ReprintsWarehouse@springernature.com.
For permissions and non-commercial reprint enquiries, please visit Copyright.com to start a request.
For author reprints, please email rob.barclay@radcliffe-group.com.
For permissions and non-commercial reprint enquiries, please visit Copyright.com to start a request.
For author reprints, please email rob.barclay@radcliffe-group.com.
- Views:
 2525
2525
- Downloads:
 0
0
- Citations: 3
Inflammation and Pre-atherosclerotic Changes in the Coronary Arteries of Children
Citation:
European Cardiovascular Disease 2006;2(2):1–3
- Abstract
- Full text
- Login or register to view PDF.
- Permissions
- References
Permissions×
For commercial reprint enquiries please contact Springer Healthcare: ReprintsWarehouse@springernature.com.
For permissions and non-commercial reprint enquiries, please visit Copyright.com to start a request.
For author reprints, please email rob.barclay@radcliffe-group.com.
For permissions and non-commercial reprint enquiries, please visit Copyright.com to start a request.
For author reprints, please email rob.barclay@radcliffe-group.com.
- Views:
 259
259
- Downloads:
 0
0
Preventative Medicine in Childhood and Adolescence - Looking for Atherosclerosis
Citation:
European Cardiovascular Disease 2006:2(2):1–4
- Abstract
- Full text
- Login or register to view PDF.
- Permissions
- References
Permissions×
For commercial reprint enquiries please contact Springer Healthcare: ReprintsWarehouse@springernature.com.
For permissions and non-commercial reprint enquiries, please visit Copyright.com to start a request.
For author reprints, please email rob.barclay@radcliffe-group.com.
For permissions and non-commercial reprint enquiries, please visit Copyright.com to start a request.
For author reprints, please email rob.barclay@radcliffe-group.com.
- Views:
 132
132
- Downloads:
 0
0